In this article we will discuss about the global sourcing funds for Indian companies.
FIIs have participated in the equity of Indian companies. Foreign Investment through ADRs/GDRs, Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCBs) is treated as Foreign Direct Investment. Indian companies are allowed to raise equity capital in the international market through the issue of GDR/ADRs/FCCBs. These are not subject to any ceilings on investment.
An applicant company seeking Government’s approval in this regard should have a consistent track record for good performance (financial or otherwise) for a minimum period of 3 years. This condition can be relaxed for infrastructure projects such as power generation, telecommunication, petroleum exploration and refining, ports, airports and roads.
There is no restriction on the number of GDRs/ADRs/FCCBs to be floated by a company or a group of companies in a financial year. There is no such restriction because a company engaged in the manufacture of items covered under Automatic Route is likely to exceed the percentage limits under Automatic Route, whose direct foreign investment after a proposed GDRs/ADRs/FCCBs is likely to exceed 50 per cent/51 per cent/74 per cent as the case may be.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Two-way fungibility of ADRs/GDRs issued by Indian Companies was permitted by the Government of India and the RBI. The RBI has now, vide APDIR Circular No. 21 dated February 13th, 2002, issued operative guidelines for the 2 way fungibility of ADR/GDR.
Earlier, once a company issued ADR/GDR, and if the holder wanted to obtain the underlying equity shares of the Indian Company, then, such ADR/GDR would be converted into shares of the Indian Company. Once such conversion took place, it was not possible to reconvert the equity shares into ADR/GDR. The present rules of the RBI make such reconversion possible, to the extent of ADR/GDR which have been converted into equity shares and sold in the local market.
This would take place in the following manner:
Stock Brokers in India have been authorized to purchase shares of Indian Companies for reconversion. The Domestic Custodian would coordinate with the Overseas Depository and the Indian Company to verify the quantum of reconversion which is possible and also to ensure that the sectoral cap is not breached. The Domestic Custodian would then inform the Overseas Depository to issue ADR/GDR to the overseas Investor.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Re-issue of ADRs/GDRs would be permitted to the extent of ADRs/GDRs that have been redeemed and the underlying shares sold in the domestic market. Two-way fungibility implies that an investor who holds ADRs/GDRs can cancel them with the depository and sell the underlying shares in the market. The company can then issue fresh ADRs to the extent of shares cancelled.
India’s Depositary Receipt Program:
India has the distinction of having the largest number of GDR issues (Rule 144A/Reg S) by any country. The first issue was by Reliance Industries ($150 million) in May 1992. Since then, the depositary receipt concept developed considerably in India with a total of 60 Indian companies raising over US$ 6.5 billion.
Earlier, Indian Companies required approval of the Government of India before issue of Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCBs). The RBI, has vide FEMA Notification No. 55 dated March 7th, 2002, liberalised these rules. Accordingly, Indian Companies seeking to raise FCCBs are permitted to raise them under the Automatic Route upto US 50 Million Dollars per financial year without any approval.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The FCCBs raised shall be subject to the sectoral limits prescribed by the Government of India. Maturity period for the FCCBs shall be at least 5 years and the “all in cost” at least 100 basis points less than that prescribed for External Commercial Borrowings.
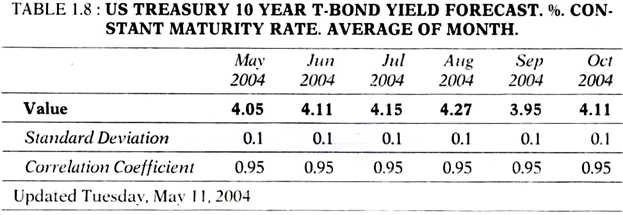
Let us now check some important benchmark interest rates in the US market:
Once the top Indian companies get cost advantage in the foreign market, subject exchange fluctuation risk, they raise money abroad. Tables 1.8- 1.11 indicates interest rates in the US market which can be compared with the Indian interest rates given in Table 1.3.
Globally Acceptable Financial Reporting System:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In view of the globalization of corporate finance and emergence globally acknowledged new generation derivative instruments in the Indian market, it becomes essentially that Indian should have a globally competitive financial reporting system. To satisfy the financial information need of the global investors and regulatory mechanism many Indian companies have started presenting financial statements in accordance with Indian GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) as well as per US GAAP.
An attempt has been made to have a set of internationally acceptable financial reporting standards. To this effect, International Accounting Standards Board has been formed abolishing International Accounting Standards Committee. The latest development is that European Union and Australia have agreed to converge with the International Financial Reporting system. Preparation is on in the US as well as in the UK. International Organization for Securities Commissions (IOSCO), whose members include securities regulatory agencies of about 100 countries, actively supports global harmonization of the financial reporting system.