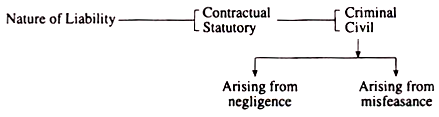
This article throws light upon the two main classification of the liabilities of a cost auditor. The classifications are: 1. Contractual Liability 2. Criminal Liability.
Cost Auditor’s Liabilities: Classification # 1. Contractual Liability:
The cost auditor is liable for non-fulfilment of the terms and conditions of an agreement between him and the company who appoints him e.g. voluntary cost audit. He may be held responsible under the Contract Act in failing to perform the duties as laid down in agreement. In the absence of any written agreement or contract, he is expected to conduct complete cost audit.
He may conduct partial audit at his own risk. Even if he does not issue an audit certificate, it does not relieve him from incurring liability.
Cost Auditor’s Liabilities: Classification # 2. Criminal Liability:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Indian Penal Code imposes a criminal liability on the cost auditor. The I.P.C. states that ‘whosoever issues or signs any certificate required by law to be given or signed or relating to any fact which such certificate is by law admissible in evidence, knowing or believing that such certificate is false in any material point, shall be punishable in the same manner as if he gives a false evidence’.
The Cost Auditor’s criminal liability may be of three categories:
(a) Falsification of books:
He shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to seven years, and shall also be liable to a fine if with the intent to defraud or deceive any person, the cost auditor:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Destroys, mutilates, alters, falsifies, or secrets or is privy to the destruction, mutilation, alteration, falsification or secreting of any books, papers or securities; and
2. Makes or is privy to the making of any false or fraudulent entry in any register, books of account or document belonging to the company.
(b) Giving False Statement:
If in any return, report, certificate or other document, he makes a statement:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Which is false in any material fact knowing it to be a material, and
2. Which omits any material fact knowing it to be a material, he shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years and shall also be liable to a fine.
(c) Giving False Evidence:
The auditor who intentionally gives false evidence:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Upon any examination, upon oath or solemn affirmation; or
2. In any affidavit, deposition or solemn affirmation in or about the winding up of any company shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend seven years and shall also be liable to a fine.
3. Liability arising from negligence:
The cost auditor may be held liable for the damages if he fails to perform his duties with reasonable skill and care, i.e. arising out of his negligence. He is liable to make good the loss or damage resulting from negligence on his part to detect defalcations or discover errors which may have caused loss to the company.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Liability arising from misfeasance:
The cost auditor may be held liable for breach of trust or responsibility and for wilful misconduct and default, depending on the circumstances of each case.
5. Liability to third parties:
The cost auditor is appointed by the shareholders in an’ annual general meeting of a company and submits his report to the Central Government and the company. He may be held liable to the Government if default is made by him in complying with the provisions of rule 3 or rule 4 of Cost Audit (Report) Rules, 1996 and shall be punishable with fine which may extend to five hundred rupees.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Liability to the professional body:
The cost auditor may be held liable for his professional misconduct if he violates the professional code of conduct as instituted by the Cost and Works Accountants Act, 1959. He is liable if he acts as a cost auditor without holding a valid certificate of practice from the Institute.